A fistula of the rectum is often formed as a result of paraproctitis, as well as other diseases of the intestinal tract. Often a person may not notice the first signs of the disease or write them off for other conditions of the body.
This behavior often causes the anal fistula to grow, fester, and the tissue around it becomes inflamed.
It is impossible to cure such a disease on its own and you will have to resort to surgery.
Characteristics of fistulas
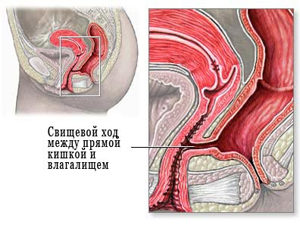
Fistulas are channels that run from the intestines to the anus, and go outside, or penetrate into neighboring internal organs. Such channels are often filled with pus and infiltrate, feces and microbes enter them. Often the inflammatory process affects neighboring tissues and other parts of the intestine. Fistulas of the rectum are classified according to several parameters.
| Classification | Kinds | Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Location of outlet | outdoor | The fistulous outlet is located near the anus, always opens outwards. |
| Internal | Fistulous passages located in the rectum end in other parts of the intestine, or go to other organs. | |
| According to the degree of distribution | Full | They have an inlet and outlet, most often found in an adult. |
| Incomplete | They have an inlet but no outlet. Considered a developing form of complete fistulas. | |
| According to the location of the fistula of the relative anal sphincter | Intrasphincteric (Intrasphincteric) | The fistulous canal begins in the rectum, and the exit is located near the anus, the fistulous canal is straight, has no tissue scarring. Occurs in 30% of cases of all fistulas, easily diagnosed even with a digital examination |
| transsphincteric | The fistula passes through one of the layers of the sphincter and has an outlet in the anus, which interferes with the act of defecation and creates great difficulties for a person. Such a fistula often has branches, as well as purulent formations near the canal. | |
| Extrasphincteric | The fistulous passage does not touch the anal sphincter area. Often such a channel looks like a horseshoe, that is, it looks like an internal fistula with a curved passage and ending in another part of the intestine or a neighboring organ. |
The passage is straight, unbranched, no tissue scarring, and no pus or infiltrate. Any rectal fistula goes through several stages of development before it becomes a difficult problem to resolve.
There are such stages of development:
- The opening at the exit of the fistula is surrounded by scar tissue that continues to grow. There is still no pus and infiltration.
- The scar tissue comes off, but abscesses appear.
- The fistulous canal has branches, a lot of abscesses. In the fistula, the presence of an infiltrate is noted.
Anorectal fistulas are a big problem for people, but if left untreated, complications can become much more of a nuisance. Therefore, it is important to diagnose a fistula of the rectum in a timely manner, best of all at the initial stage of development, then it will be better treated.
Causes of fistulas of the rectum

Systematic untreated constipation leads to the formation of fistulas.
Anorectal or pararectal fistula most often appears after the transferred and untreated paraproctitis. But there are also other causes of fistulas of the rectum, namely:
- a surgical error when paraproctitis is treated, but the affected areas are not completely removed during the operation;
- bowel disease (Crohn's disease, diverticulitis, anal fissures, hemorrhoids);
- complications after the hemorrhoid is removed - muscle fibers are sutured;
- rectal injuries received independently or during diagnostic medical procedures;
- chlamydia, syphilis;
- intestinal tuberculosis;
- malignant neoplasms in the intestines, especially in the rectum;
- postpartum trauma in women.
Often the problem is aggravated by long-term chronic constipation, when the fistula only appears, the feces, which cannot leave the body in a timely manner, begin to clog this passage and release toxins. This contributes to a more active development of the fistula, as well as aggravating the complexity of the process itself.
Symptoms

The symptoms of this pathology are often so pronounced that it is simply impossible to confuse them with signs of other diseases. Patients complain about:
- pain in the lower abdomen, as well as in the rectum, pain in the anus intensifies during the act of defecation;
- discharge from the exit of the fistula of pus, which is noticeable on clothes and underwear;
- deterioration in the condition of existing anal fissures or the formation of new ones;
- weakness and decreased performance;
- the presence in the feces of impurities of blood and pus, a characteristic non-specific odor;
- irritation of the anus with discharge from the fistula, the appearance of a rash on the skin in the anal and perianal region;
- increase in body temperature;
- pararectal fistulas can lead to inflammation of the female genital organs, which will be accompanied by pain and discharge of pus from the vagina;
- problems with sexual life in men.
Patients rarely endure such symptoms for a long time, so they try to seek help from a proctologist for excision of the fistula in order to get rid of the tormenting problem, as well as eliminate other signs of rectal disease.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing a fistula of the rectum is quite simple even at the time of collecting anamnesis and digital examination of the intestine. However, doctors use additional diagnostic measures to confirm the diagnosis, as well as to establish the causes of the formation of passages and the detection of concomitant diseases.
These include:
- Sigmoidoscopy - examination with a probe of the rectum.
- Colonoscopy - examination of the rectum and large intestine with a probe with the possibility of taking material for a biopsy.
- Ultrasonography is an examination of the rectum using an ultrasound machine, when the tube itself is inserted into the intestine and ultrasound is delivered from the inside.
- Staining of the anus - with the help of a dye injected into the rectum, a fistula can be detected by observing the filling and distribution of the substance through the intestines.
- Fistulography - an x-ray of the rectum is taken using a contrast agent.
- - allows you to find out the performance of the sphincter of the anus.
- Microbiological examination of discharge from the rectum or directly from the fistula itself - allows you to establish the presence of a bacterial infection associated with the disease.
- CT is performed if the fistula has given complications to neighboring organs.
These diagnostic methods allow you to establish an accurate diagnosis, as well as identify the cause of the fistula, if there are extraneous bowel diseases. It is also necessary for the doctor to tell how to treat not only the fistula itself, but also its other complications or concomitant diseases.
Treatment
It is impossible to cure a fistula of the rectum at home with folk remedies. Even medicines do not always give a positive result. Whether the fistula can pass or take place? This is unlikely, it is impossible to hope for luck here, since the consequences of this pathology, if left untreated, can be fatal for a person. The main treatment for a fistula is surgery.
Treatment without surgery is in one option - pouring fibrin glue into the fistulous passage until it is completely filled, followed by suturing both openings of the intestinal fistula. However, such treatment does not guarantee complete recovery and the absence of re-formation of fistulas, especially if the original cause of the disease is not eliminated.
Operation
Surgical treatment consists in excision of the fistula, as well as drainage of abscesses. During excision, it is important not to touch healthy tissues and be extremely clear - limit yourself to the affected area. The operation to remove the fistula of the rectum takes place under general anesthesia and is painless for the patient, which cannot be said about the postoperative period.
Video
It is also possible to carry out such an operation with a laser. This will take less time and reduce the risk of infection, the patient will be able to return to their normal lifestyle in the very next few days. However, this operation is more expensive.
The postoperative period is an important part in the process of recovery and prevention of relapses.
At this point, you need to follow the rules:
- in the first three days there was no defecation, so the patient can hardly eat, you can only drink decoctions and water, glucose is administered intravenously. This is done to prevent injury to the closed canal by stool.
- food was further liquid and in small portions, so that the feces were soft and did not injure the intestines;
- the patient complied with bed rest, did not lift weights;
- dressings were regularly performed, you can use an ointment with an anesthetic effect to relieve pain after surgery.
Treatment takes about two weeks, so that a relapse of the disease does not occur, it is necessary to establish what causes the fistula in this case, and try to avoid this factor, or treat the existing disease that provokes this phenomenon.
Complications
The fistula of the rectum is very dangerous for its complications. If purulent contents enter the abdominal cavity, peritonitis may develop, which is often fatal. Also, due to the fistula, bleeding is possible, which can lead to anemia. Intoxication of the body with stagnant feces, when the fistula interferes with its exit, can adversely affect the general well-being of the patient, as well as the functions of other organs.
If scars are formed in large numbers, this can threaten the disruption of the sphincter, which will further lead to fecal incontinence. Also, in certain cases, a fistula can cause a malignant neoplasm.
So that the disease does not bring significant harm to the body, it must be treated immediately, without delay. A fistula of the rectum has a good chance of a complete remission without a return of the disease. If the operation is carried out in time, then the person retains full working capacity and normal health.
Video
Fistula - a narrow canal lined with granulations or epithelium that connects an organ, cavity, or deep-lying tissue to the surface of the body. Fistulas can also connect hollow organs to each other. Reasons for the development of fistulas: inflammatory processes, tumors, trauma, malformations, foreign bodies, malnutrition of tissues.
Depending on the cause that caused the fistula, the discharge may be of a different nature: purulent, tissue decay products, organ secretion, the contents of a hollow organ (urine, intestinal contents, etc.).
Exists several classifications of fistulas depending on the principle underlying the division.
I. By origin, fistulas are distinguished: congenital, acquired.
II. In relation to the external environment: external and internal.
III. By structure: granulating, epithelized, labial.
IV. By the nature of the discharge: urinary, salivary, fecal, cerebrospinal fluid, purulent, mucous, etc.
Congenital fistulas are the result of malformations of embryonic development. The most common are median, lateral fistulas of the neck, fistulas of the navel, etc.
Acquired fistulas can be caused by a pathological process, for example, in chronic osteomyelitis, tuberculosis of bones, joints, tissue destruction by a tumor (vesicouterine fistulas in uterine cancer, etc.). In addition, they are formed as a result of trauma (fistulas Bladder, bronchial fistulas, etc.) or operations (failure of sutures, etc.). In a number of patients, fistulas are formed surgically to improve the function of the organ, to ensure the outflow of discharge when it is impossible to remove the diseased organ, etc.
External fistulas connect hollow organs, cavities or a focus of infection in soft tissues and bones with the external environment. Internal fistulas connect hollow organs - a hollow organ and a cavity or a hollow organ and a pathological focus.
With granulating fistulas the entire surface of the fistulous tract and the walls of the pathological focus connected to the fistulous tract are covered with granulation tissue. Prevents the normal growth of granulations and the healing of the fistula D.C. along the fistulous course of the wound discharge. The destructive effect on granulation of chemically active secrets (duodenal fistula, lactiferous fistula, etc.) creates conditions for the penetration of toxins and microbes into the surrounding tissues, which causes reactive inflammation and leads to the formation of a large number of scars around the canal of the granulating fistula.
With the weakening of the body's defenses, it is possible for the infection to spread to the surrounding tissues and even its generalization. With epithelialized and labial fistulas the epithelium lining the fistulous tract passes directly into the epidermis of the surrounding skin, as a result of which there is no defect in the integument. This prevents the development of local and general surgical infection.
Symptomatology and clinic determined by the nature of the fistula, its localization. A congenital median fistula has a small opening and a mucous discharge. With a labial intestinal fistula, there is an abundant discharge of intestinal contents. The nature of the discharge from the fistula determines the condition of the surrounding skin. Dermatitis often forms around the gastric or duodenal fistula due to the corrosive action of digestive juices. With urinary fistulas, swelling of the surrounding skin is often noted, followed by the development of elephantiasis. The general reaction of the body is not the same for various fistulas. Violations of the general condition can be observed with secondary infection through a fistula, with difficulty in the outflow of contents in purulent fistulas, with a large loss of digestive juices (violations of protein, water-salt metabolism, etc.).
Fistulas of hollow organs lead to pronounced dysfunctions of organs, accompanied by leakage into the organ of a secret that is not characteristic of it (food in the bronchus with a broncho-food, intestinal contents in the bladder with an enterovesical fistula, etc.).
The peculiarities of the course of fistulas include the fact that epithelializing and labial fistulas do not spontaneously heal, and granulating fistulas can heal on their own if the body copes with the infection, and necrotic tissues (sequesters, etc.) stand out from the pathological focus.
With fistulas of hollow organs, an important condition for its self-closing is to reduce the release of contents through it.
Diagnostics. Diagnosis of a fistula is usually not difficult. It is based on characteristic complaints, anamnesis, type of wound, amount and nature of the discharge, and in case of interorgan fistulas, on a change in the function of the diseased organ.
To clarify the direction of the fistulous passage, its length, the number and nature of the branches, the connection with the pathological focus, etc., probing, X-ray examination with the introduction of various contrast agents (sergozin, iodolipol, etc.) into the fistulas is used. Clarification of the diagnosis is facilitated by the study of the discharge for the presence of hydrochloric acid (if gastric fistula is suspected), uric acid salts - with urinary fistula, etc. The introduction of paint (for example, methylene blue) into the pleural cavity in case of suspected bronchopleural fistula allows you to establish sputum staining. The introduction of dye into the fistula of the anus makes it possible to confirm the hollow fistula by detecting staining of the contents of the rectum, etc.
Fistula treatment:
a) Conservative treatment: granulating fistulas can heal on their own when the outflow of organ contents through them stops. Of great importance is the prevention of the development of infection (the use of antibiotics parenterally and locally in the form of injections with novocaine). To prevent irritation of the skin around the fistulas, it is necessary to thoroughly cleanse it during dressings, lubricate with sterile vaseline or Lassar paste. If the protein electrolyte balance is disturbed, it is important to regularly transfuse blood, plasma, protein substitutes, electrolyte solutions (sodium, potassium, etc.). At the same time, general strengthening therapy is carried out (high-calorie nutrition, vitamins, glucose infusion, etc.).
b) Surgical treatment is indicated for epithelized, labial fistulas, with long-term non-healing granulating fistulas. The main thing in the surgical treatment of epithelized fistulas, in addition to the elimination of the focus, is the complete removal of the epithelial cover of the fistulous tract.
In labial fistulas, the hollow organ is separated from the surrounding tissues along the entire circumference of the fistula, the hole is sutured so that the mucous membrane and epithelium are screwed into the lumen of the hollow organ and do not fall between the contacting surfaces of the organ to be sutured. With large cicatricial changes in the walls or a pronounced narrowing - the lumen of the intestine, sometimes resort to resection of the organ.
With granulating fistulas, the operation aims to eliminate the focus of inflammation in the depths of the tissues with the obligatory removal of sequesters, dead tissues, foreign bodies, etc., as well as the creation of a good outflow of wound discharge not through the fistulous tract.
c) Postoperative treatment of fistulas involves the fight against infection (antibiotics), detoxification therapy (blood transfusion, plasma, administration of glucose, vitamins, etc.), general strengthening treatment (high-calorie nutrition, spa treatment, etc.), physiotherapy (UHF, ultraviolet irradiation and etc.)
Handbook of Clinical Surgery, 1967.
, fistula (from Latin this word is translated as "tube") - this is a channel that connects hollow organs to each other either with the external environment or connects the tumor to the cavity or surface of the body. As a rule, the fistula looks like a narrow channel, covered .
It is customary to distinguish fistulas that appeared as a result of certain pathological processes, as well as fistulas, as a result of a surgical intervention performed in order to divert the contents of a certain hollow organ.
Fistula on the gum
Fistula on the gum - This is a complication of chronic, which is especially common. If we evaluate that disease in terms of its severity, then it is considered the most dangerous, because after this illness it lasts a very long time, and it is also important to find out what exactly provoked its manifestation.
The progression of the disease provokes the growth of granulation. This is a benign connective tissue that disrupts the healing process. Bacteria multiply in this place, because of which pus begins to stand out. If you start treating the disease in the initial stage, then you can get rid of the disease relatively quickly.
But in the absence of adequate timely treatment, a fistula on the gum provokes the destruction of the gums directly around the tooth, and later of those soft tissues that are located nearby. With the development of a fistula, pus is abundantly released, as well as fluid with blood. In this case, granulations germinate under the alveolar process (the so-called bone bed of the tooth). Subsequently, a violation of the mucous membrane occurs in this place, and as a result, a fistulous passage appears.
The main danger of this disease is the possibility of damage to the soft tissues of the face. In the absence of adequate treatment, the fistula grows outward: it mainly exits through the cheek. As a result, a person has a noticeable facial defect.
Another reason for the development of a fistula on the gums in humans is the poor quality of treatment.
When the dentist intends, he must thoroughly clean the carious cavity, remove all areas of the tooth that have been affected by caries, and disinfect. If some action was performed poorly, then the infection gets inside the tooth, which was sealed. Microorganisms are actively developing, and the person suffers from pain and subsequent inflammation around the gums.
Diagnosis of a fistula on the gum is carried out by a dentist. But for a more detailed examination of the features of the disease, an X-ray examination should be performed. Indeed, during a visual examination, it is not always possible to determine how serious the disease is and what its scale is at the moment. On an x-ray, you can see how deeply the gum is affected, whether there is pus in other areas, and whether the periosteum has begun to be damaged. Only when all these points are determined, it is possible to prescribe competent treatment and achieve an effective result.
If the fistula on the gum appeared due to periodontitis , then to eliminate the problem, it is necessary, first of all, to treat the cause of the disease. Initially, the doctor cleans the canals of the tooth from carious deposits, pus, after which the tooth cavity is cleaned and treated with an antiseptic. After that, the doctor puts a seal. After the end of this stage of treatment, the acute manifestation of the disease can be partially muffled. This is followed by the stage of getting rid of microorganisms, for which the patient is prescribed special preparations in the form of ointments and pastes.
Today, many modern methods of fistula treatment are used: ultrasound method, laser exposure, cauterization with current. It is also mandatory to carry out drug therapy. In this case, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, often used .
If the fistula on the gum has severe form In this case, the patient is scheduled for surgery. Even if a person does not feel pain, pus comes out through the fistulous tract, then after a while the pus still enters the periosteum. If the periosteum is damaged, the operation must be done as soon as possible. Therefore, the course of the disease without pain is considered the most dangerous. With such a development of the disease, doctors try to save the patient's tooth, as well as to avoid later pronounced gum defects. Also, the surgical method of treating a fistula is used if the granulation grows too much.
Therefore, it is very important to seek help in time, because with a competent approach to treatment, the fistula closes already for a week.
To make rehabilitation after an illness faster, it is recommended to use some folk methods. For example, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with a salt solution, decoctions of sage, chamomile, eucalyptus.
Fistula of the rectum
 Fistula of the rectum
a disease also called chronic
, in which inflammation occurs in the anal crypt, pararectal tissue, intersphincter space. At the same time, a fistulous tract is formed, the affected crypt acts as an internal opening. With a fistula, infection occurs from the intestinal lumen. In the purulent passage, a wall is formed from the connective tissue. As a rule, the external opening of the fistula is open on the perineum. The diameter of the fistula in most cases is no more than one millimeter. Fistula of the rectum often occurs as a postoperative, post-traumatic phenomenon.
Fistula of the rectum
a disease also called chronic
, in which inflammation occurs in the anal crypt, pararectal tissue, intersphincter space. At the same time, a fistulous tract is formed, the affected crypt acts as an internal opening. With a fistula, infection occurs from the intestinal lumen. In the purulent passage, a wall is formed from the connective tissue. As a rule, the external opening of the fistula is open on the perineum. The diameter of the fistula in most cases is no more than one millimeter. Fistula of the rectum often occurs as a postoperative, post-traumatic phenomenon.
In most cases, a fistula of the rectum manifests itself in a person after a previous acute paraproctitis.
As a rule, a person turns to a specialist with complaints about the presence of a wound (which is a fistulous opening) near the anus. Usually, pus, ichor is constantly released from this wound, so the person experiences severe inconvenience. Often the discharge is very strong, therefore, due to their constant appearance, the skin near the fistulous opening itches and is irritated.
If fistula full and, accordingly, is well drained, then the pain of a person does not bother. It manifests itself when incomplete internal fistula rectum. As a rule, the pain occurs during a bowel movement, and after it begins to gradually subside. Most often, the disease has an undulating course. Sometimes, with a fistula, the inflammatory process in the pararectal tissue is exacerbated. Inflammation is manifested as a result of blockage of the fistulous passage by granulation tissue or purulent-necrotic masses. As a result of such phenomena, , which is later opened, and after emptying the patient's condition improves. But the wound still remains - it has a diameter of no more than one centimeter. Through this external opening of the fistula, pus comes out further.
During remission, the patient does not feel pain, and if he carefully observes all the rules of hygiene, then the fistula at this time may not cause him any inconvenience. However, during exacerbations, the condition deteriorates sharply. In addition to pain and inconvenience in the area of fistula formation, the patient suffers from asthenia, headache, and sleep disturbances. There may be mental problems and in men.
If a person has a fistula of the rectum, complicated by the presence infiltrates and purulent cavities, exacerbations occur quite often. Respectively, general state a person can get worse. In addition, there are severe changes of a local nature: the perineum, the anal canal can be deformed, the muscles that compress the anus change. The result of all these phenomena is anal sphincter insufficiency . Also, as a complication of the disease, pectenosis may occur, which is characterized by the appearance of scars in the wall of the anal canal. If the fistula is not treated for many years, the disease can become malignant.
Diagnosis of a fistula of the rectum
As a rule, the diagnosis of a fistula of the rectum is carried out after the patient turns to a specialist with the corresponding complaints. The doctor initially conducts an external examination, in which an external opening is detected (provided that the patient has a complete fistula). After that, palpation of the perineum and perianal region is performed. The doctor also conducts a digital examination of the rectum and anal canal. The specialist examines the patient's history in detail.
After that, the attending physician prescribes other studies: for a fistula of the rectum, a test with a dye is used, probing the fistula. Also, every patient with a fistula must undergo sigmoidoscopy in order to determine the condition of the rectal mucosa, as well as to detect other diseases.
Sometimes X-ray examination is used as an auxiliary diagnostic method. It is also important to differentiate the fistula from pararectal tissue cysts, actinomycosis, and other types of fistulas.
Treatment of a fistula of the rectum
The diagnosis of "fistula of the rectum" is a condition in which there is a direct indication for a surgical operation. An important point in the treatment of rectal fistula is the time of such an operation. When determining the duration of the operation, it is important to consider clinical course ailment. So, if there is an exacerbation of the disease, and an abscess has formed, you should first open the abscess and eliminate the purulent process.
However, the operation should not be postponed for a long time, because the exacerbation will be repeated periodically. As a result, scarring and subsequent deformation of the perineum and anal canal may occur.
If infiltrates occur along the course of the fistula, then the doctor prescribes a course of anti-inflammatory treatment for the fistula. In the process of therapy, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, a course of physiotherapy. After the elimination of infiltrates, the patient is prescribed a surgical operation. However, the operation is performed only when the fistula is open.
There are several different types operations that are prescribed to patients with a fistula of the rectum. So, it is possible to dissect a fistula into the lumen of the rectum, excise the fistula into the lumen of the rectum, followed by opening and draining the streaks, similar excision of the fistula and suturing the sphincter, etc.
to choose best method operations, the doctor is guided by some points. First of all, it matters where exactly the fistulous passage is located relative to the external sphincter of the anus. It is also important to take into account how developed the cicatricial process is, as well as whether there are purulent infiltrates and cavities in the pararectal tissue.
 It is important that the operation is performed by an experienced coloproctologist in a specialized hospital. If there is a sharp exacerbation of chronic paraproctitis, then an urgent operation can be performed in a general surgical hospital. However, subsequent treatment should be carried out by a highly specialized doctor due to the high risk of complications.
It is important that the operation is performed by an experienced coloproctologist in a specialized hospital. If there is a sharp exacerbation of chronic paraproctitis, then an urgent operation can be performed in a general surgical hospital. However, subsequent treatment should be carried out by a highly specialized doctor due to the high risk of complications.
Most often, after surgery in patients, a fistula recurrence occurs as a complication, and anal sphincter insufficiency may also occur. The recurrence of the disease occurs due to the erroneous choice of the method of operation, its incorrect conduct, and also due to the occurrence of errors in the postoperative recovery of the patient.
As a rule, with a fistula of the rectum, the prognosis is favorable, unless we are talking about fistulas, which are characterized by relapses, prolonged inflammation, cicatricial changes in the sphincter, intestine, pararectal tissue. Therefore, for a complete cure, it is important to perform a surgical operation on time.
Fistula prevention
To ensure the prevention of fistula of the gums, it is important to eliminate all problems with the teeth in time and do this only with the help of professional specialists. Exists general rule that each person should have a dental check-up twice a year. Also, with a certain frequency (once every few years), it is necessary to take diagnostic pictures of teeth that have previously been treated in order to prevent possible complications as early as possible.
In addition, to prevent the formation of fistulas, it is important to maintain the proper level of immunity.
Causes of the formation of fistulas of the anus and ways to get rid of the disease.
Why does a fistula of the rectum occur? How to alleviate the patient's condition? Is it possible to do without surgery and how to cure a fistula? Features of the manifestation of pathology in children. This article will elaborate on these issues.
What is a rectal fistula?
Fistulas or fistulas of the rectum (fistulae ani et recti) is a serious pathology associated with the formation of purulent passages through the connective tissue of the rectum. The exit of the fistulous tunnels may end in the perirectal tissue. This - incomplete internal fistulas. More often, the passages are completely open and open through the skin in the anus area, the so-called complete external fistulas.
Rectal fistulas usually appear as a result of an adrectal abscess of the rectum, which has a medical name - paraproctitis. Fistulous passages can be classified by location and degree of prevalence.

Usually there are complete fistulas. They have two openings on both sides: inlet and outlet. There are fistulas with several entrances. Incomplete fistulas with one inlet often turn into full fistulas due to the gradual dominance of microorganisms in them.
Infected tissue cells lose their tone and are gradually destroyed: there is a breakthrough of the fistula outward with access to the surface of the skin around the anus. The appearance of fistulous openings in the anus can also be associated with such diseases:
- diverticulitis (inflammation of the lining of the large intestine)
- rectal tuberculosis
- syphilis
- chlamydia
- Crohn's disease
What is dangerous fistula of the rectum, what could be the consequences?

Which have not been treated for a long time and have become chronic, are fraught with many general complications: from purulent processes of blood infection to the possibility of developing carcinomas (cancerous tumors) of the anal ducts. Untreated anal fistulas can lead to scarring that causes pain during bowel movements and gas.
How to determine the fistula of the rectum: symptoms

Complete external fistulas appear visually: on the skin around the anus and partially on the buttocks, one or more seals of tissue with an internal lumen are palpated.
Through this passage, discharge of pus, mucus or infiltration is observed. In places where the fistula exits, the skin becomes moist, softened, loses its natural turgor due to maceration. When palpating the rectum, a funnel-shaped opening-fistula is found.
Availability incomplete internal fistulas causes patients to feel the presence of a foreign body in the anus. With insufficient exit of the infiltrate from the fistula cavity, patients feel:
- pain and discomfort in the anus
- retention of stool and urination
- discharge from the rectum (pus, infiltrate, mucus)
- irritation and redness of the skin around the anus and part of the buttocks
- fever, chills
Fistula of the rectum in a child: causes
- Diseases in the form of rectal fistulas are rare in childhood. This pathology is most often at the birth of a child and is the result of failure. prenatal development fetus for any reason.
- The disease may appear when Crohn's disease(a genetic disease that affects the entire gastrointestinal tract) or after suffering an acute paraproctitis(purulent inflammation of the tissues adjacent to the rectum).
- Before prescribing treatment, you should know the root cause of fistula formation. Congenital ones require surgical treatment, as the disease threatens the life of the baby. The operation consists in removing the focus of inflammation and the surrounding epithelium, captured by the pathological process.
- If fistulas are found in a baby in the first months of life, surgical intervention can be postponed to a later date - when the child reaches 18 months. This is possible only with a stable condition of the child without the spread of infection, accompanied by an increase in temperature and a deterioration in the condition of the baby.
Parapractic fistula after paraproctitis: causes

paraproctitis is the main cause of rectal fistulas. There is inflammation of the pararectal tissue of the rectum with infection through the anal glands and damaged mucosa.
The inflammatory process is transmitted through neighboring diseased organs. Most often, paraproctitis accompanies the following diseases:
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- inflammation of the prostate and urethra
- inflammation of the female genital area
- pelvic osteomyelitis
Fistulas of the anus may appear due to:
- running paraproctitis
- complications during operations with paraproctitis
- unsuccessful surgical opening of paraproctitis
- spontaneous opening of paraproctitis
Fistula of the rectum - treatment without surgery at home
IMPORTANT: Complaints of pain and discomfort in the area of the rectum are the reason for contacting a proctologist for a consultation.
- Symptoms of the manifestation of the fistula of the rectum cause great discomfort in the life of the patient. It cannot be cured at home, there is no universal remedy for scarring fistula tunnels. At home, you can only alleviate the patient's condition with the help of medications and traditional medicine: ointments, herbal lotions and fees.
- Folk recipes have been developed for a long time and have been tested on more than one generation of people. Ointments and poultices relieve pain, cleanse and disinfect the skin, remove inflammation in the foci of fistula breakthrough.

Fistula of the anus - treatment at home
- The use of medicines at home is not a solution to the problem of rectal fistulas. Painkillers, antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory drugs relieve the symptoms of an anal fistula only for a while.
- Then the exacerbation of the disease begins again, requiring an urgent visit to the doctor. After clarifying the diagnosis, an algorithm for treating the patient is built depending on the severity of the disease.
- At the first stage, antibiotics are prescribed to suppress the infectious process and drugs that alleviate the patient's condition - antispasmodics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Subsequently, surgical intervention is required after a series of necessary tests and a complete examination.
For in-depth diagnosis of the disease, methods are used:
- sphincterometry (assessment of the working condition of the anus sphincter)
- irrigoscopy (intestinal examination using x-rays)
- computed tomography (layered examination of the intestine by means of x-rays)
- fistulography (X-ray examination fistulous passages using radiopaque agents)
Folk remedies for the treatment of rectal fistula

Exist folk recipes alleviate the condition of the patient with external perforation of the fistula. Let's share some.
St. John's wort lotion
The procedure with a lotion of St. John's wort helps to remove purulent contents from the fistula opening. Regular application of herbal compresses to the sore spot relieves inflammation and irritation, helps to cleanse the passage, remove itching and pain.
- Three tablespoons of finely chopped raw materials - St. John's wort herbs are steamed with 200 ml of boiling water.
- Insist on a steam bath for 5-7 minutes.
- The steamed slurry of grass is laid out on a piece of linen fabric.
- The lotion is applied in a warm state to the inflamed area and covered with a piece of cellophane film.
- The procedure is carried out daily until the pus is completely discharged.
Lotion with mummy and aloe juice
- A 3% aqueous solution of mummy is prepared: 3 g of mummy is dissolved in 100 ml of warm purified or boiled water.
- A tablespoon of 3-year-old aloe leaf juice is added to the dilution.
- A piece of gauze is abundantly moistened with a solution and applied to a purulent focus.
Lotions from kombucha with plantain roots
- Boil a tablespoon of plantain roots in 200 ml of water.
- After cooling, 200 ml of kombucha infusion is added to the broth.
- A gauze pad is moistened with medicine, slightly squeezed out and applied as a lotion to the exit of the fistulous opening.
Warm sitz baths with infusions of oak bark, chamomile and calendula flowers, sage leaves help relieve inflammation and irritation of the skin around the anus.
Ointment for the treatment of rectal fistula

An ointment prepared with herbs helps to cleanse the inflamed surface of the skin around the fistulous opening, relieve swelling, remove redness and irritation. In general, the ointment has a beneficial effect and heals the fistulous tunnel.
- Herbal ingredients: oak bark, water pepper grass, flax flowers are used in equal proportions. 2 tablespoons of the herbal mixture is finely ground, for this you can use an electric coffee grinder.
- Herbal powder is poured with two tablespoons of melted fresh pork lard.
- The ointment is kept in the oven at a minimum temperature of 3 hours.
- Gauze swabs are impregnated with ointment and applied to the inflammatory focus for 5 hours, then the swab is changed to a new one.
Operation to remove the fistula of the rectum: reviews
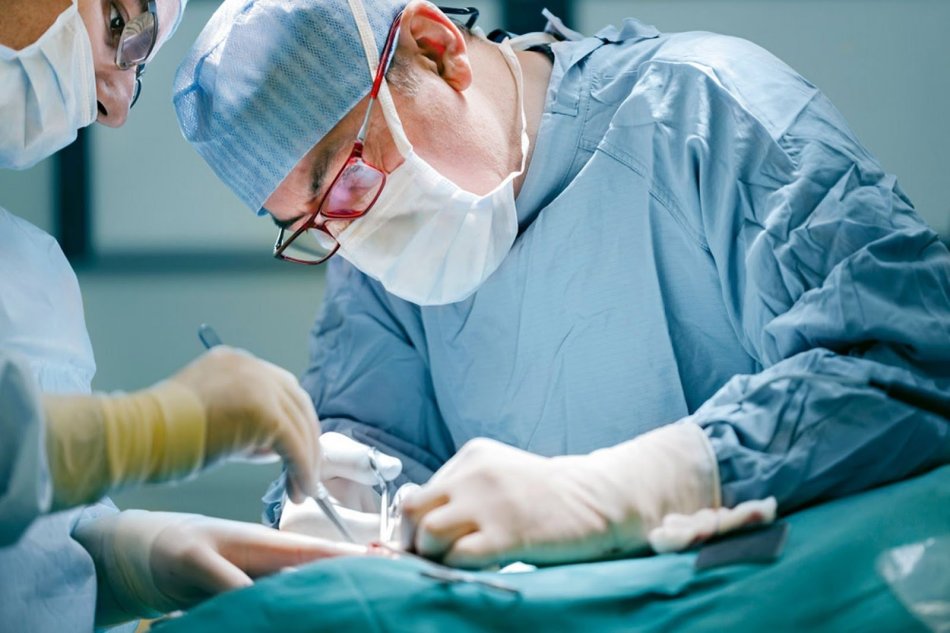 Surgery is the main way to get rid of rectal fistulas
Surgery is the main way to get rid of rectal fistulas Rectal fistulas cannot resolve themselves on their own. Pathology is not amenable to conservative treatment. Drug therapy and procedures in the form of baths, compresses and lotions relieve the patient's suffering for a short time.
This should be taken into account in complicated forms of the disease, when it passes through the muscle tissue of the anus sphincter, the so-called trans- and extrasphincter fistulas.
IMPORTANT: Rectal fistulas are not prone to complete healing without surgery.
Tasks of surgical treatment of rectal fistulas
- Removal of the internal fistula.
- Opening and removal of the pararectal abscess focus.
- Excision of the fistulous passage.
- The use of minimal impact on the external sphincter of the anus to prevent the loss of its performance.
- Postoperative conservative wound healing with minimal scarring.
- The operation to remove the fistula of the anus is performed under general anesthesia. The wound after excision of the fistula, as a rule, heals quickly. On the 5-7th day, the patient is discharged if the healing process goes according to plan and without complications. In the first hours after the operation, pain in the wound area is possible.
- After the fistula is removed, the patient is prescribed a complex of medications for internal and local use in the form of suppositories, ointments, wound healing drugs and anti-inflammatory tablets. The patient is under medical supervision until complete recovery.
- During the period, it is important to perform hygiene procedures. It is allowed to take a shower and sitz baths with herbal infusions of chamomile, calendula, sage, oak bark. Baths are recommended after each act of defecation.
In everyday vocabulary, a fistula is a through hole, hole or void. In medicine, the fistula has another name, literally integrated from Latin - a fistula (that is, a tube). It can be a deep wound with a narrow opening or a canal connecting different cavities. Usually the fistula is lined with epithelium and unites the tumor or hollow internal organs with the surface of the body. Sometimes fistulas appear that penetrate between the internal cavities, and fistulas are also specially made during surgical operations, thus preparing the way for the subsequent removal of the contents of a certain cavity.
A fistula is a deep wound with a narrow opening or a canal connecting different cavities.
As a rule, fistulas are named depending on their location. Thus, there are various fistulas - from dental to coccygeal.
- Bronchial fistula is formed in the bronchi and is manifested by the pathological communication of this organ with the pleural cavity.
- Gastric fistula does not exist in nature and is the result of the activities of surgeons. Usually created during gastric resection or as an alternative to radical surgery on the esophagus.
- The duodenal fistula is located in the duodenum, and rectovaginal fistula damages the septum.
Rectal fistulas are of two types:
- anorectal;
- pararectal.
Fistula on the gum
A fistula on the gum is formed as a result of the development of another disease associated with infection of the tooth or gum.
It is believed that there are three main causes of dental fistula:
Video
Fistula of the rectum
The fistula of the rectum appears as a result of inflammation of the anal crypt. This happens in the mucous membrane of the anal canal. Usually a fistula occurs after acute paraproctitis, that is, an abscess. Even if the patient turns to the doctor in a timely manner when purulent discharge is detected, it is not always possible to perform a surgical operation. In such cases, physicians are limited to opening and cleaning. Drainage allows you to get rid of the infection, but does not eliminate the internal opening of the fistula inside the rectum.
The external opening of the fistula of the anus usually opens near the anus. Given the location and sensitivity of the skin in this area, the presence of a fistula rarely goes unnoticed. Sucrose and pus secretion often accompany the development of the disease, therefore, for effective treatment in parallel, daily baths and regular washings are prescribed.
Damage to the mucous membrane of the rectum and a violation of its elasticity are the most negative consequences of a neglected condition. In the presence of complications and abundant inflammation and the appearance of several fistulas in parallel, a general decrease in immunity, an increase in body temperature, the development of nervousness and headaches are possible.
Anal fistula is a very unpleasant, constantly irritating disease. And only timely treatment started guarantees a successful recovery and getting rid of such an unpleasant disease. Diagnosing a pararectal fistula is not always easy, since only the external exit of the canal is visible during external examination.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a number of manipulations are usually performed:
- external examination and palpation;
- probing to determine the size and direction of the fistula;
- a test with dyes makes it possible to find out the type of fistula. If the fistula is incomplete, staining of the rectal tupfer does not occur;
– ultrasonography;
- sphincterometry, checks the function of the sphincters;
- sigmoidoscopy reveals inflammation, hemorrhoids, tumors and cracks.
Treatment of anal fistula is always surgical, so preparation for surgery requires a thorough and comprehensive check of health conditions. Treatment at home is unacceptable, so do not delay the visit to the doctor.
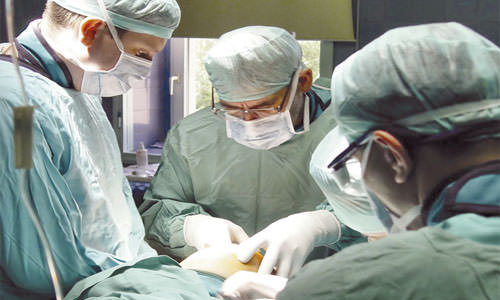
Anal fistula treatment is always surgical
The technique of the operation depends on the type of fistula, the number of scars and inflammatory changes. A qualified proctologist will select the correct, adequate treatment, taking into account the patient's individual history and examination results. During the rehabilitation period, in addition to standard therapy, baths with herbal decoctions can be used as auxiliary procedures. Folk remedies will become an antiseptic and help relieve itching and irritation at the site of healing of the postoperative scar. Discuss specific recipes and options for decoctions with your doctor.
Video
Fistula on the coccyx
A fistula on the coccyx is not a frequent phenomenon, but a serious one. The coccyx itself is formed from several extreme, fused discs of the spine and is characterized by immobility. It is to this zone of the vertebrae that the muscles and ligaments that affect the functioning of the intestinal system and the bladder are attached. The causes of the inflammatory process and the appearance of the coccygeal fistula may be different, and sometimes it is a whole complex of prerequisites that chronically affect the body.
Among the main factors provoking the growth and development of the fistula, there are:
- spinal injuries;
- large physical exercise;
- nerve entrapment lumbar spine;
- infectious diseases;
- hypothermia;
— sedentary image life.
Of course, in the aggregate, these causes lead to a general weakening of the body, the rapid spread of infection and, as a result, the formation of a fistula. Congenital pathology involves the growth of a cyst of the coccyx, otherwise referred to as a fistula on the coccyx, but the process of formation of such a deviation is fundamentally different from the typical development of the disease.
In addition to pain, the main sign of the presence of a fistula is the discharge of pus from some part of the coccygeal zone. In addition, inflammation of the skin in the same area and even a sharp increase in temperature are possible. In the stage of inflammation, the fistula looks like an abscess and constantly increases in size. The outflow of pus does not imply the proximity of recovery, since the infection is inside the fistulous canal and is not excreted along with the discharge.
A neglected fistula on the coccyx can have negative consequences, so a visit to the doctor is very desirable. As a complication, an abscess, eczema and the spread of fistulas, gradually penetrating the entire coccygeal region of the body, can be diagnosed.
The only generally recognized effective method The treatment for coccyx fistula is surgery. Only surgically it is possible to clear the canal from infection, block the edges of the fistula and locally dissociate the body from the inflammatory process. In parallel with this, the doctor conducts drug treatment aimed at reducing inflammation and general immunity support.
To reduce the risk of recurrence, patients are admitted to hospital for treatment and kept during the rehabilitation period. The use of an ultrasonic scalpel and modern biological tissue welding during radical surgery gives excellent results and minimizes the consequences of tissue damage. Wound defects after fistula surgery are usually closed using plastic surgery methods, therefore, in many cases, the postoperative appearance of the external integument in patients is quite natural.
Fistula behind the ear
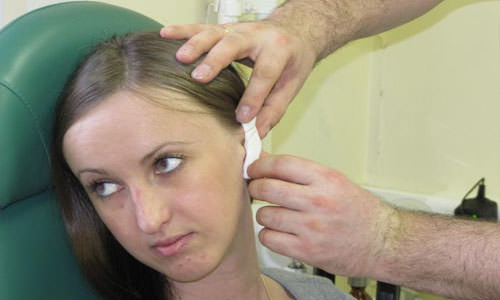
The standard location of the ear fistula is the area of the cartilaginous protrusion near the base of the ear shell
A fistula behind the ear (pinna) most often occurs congenitally and in utero as a result of defective formation of the rudiment of the gill arches or directly in the cartilaginous tissue of the ear. Under the influence of certain factors, such a fistula can periodically become inflamed, acquiring a chronic form.
The standard location of an ear fistula is the area of a cartilaginous protrusion near the base of the ear shell. The diameter of the channel and its depth can be different, while the shape is almost always sinuous. Given that this is more of a cosmetic defect, the patient learns about the presence of a fistula only after its blockage and the appearance of typical signs of the disease. With the constant release of pus and secretion, the passage gradually narrows, and as soon as the external exit is blocked, an inflammatory process begins inside.
From the moment the pain appears, there are suspicions and a close examination of the future patient at home. The doctor carries out the outflow of pus with a small incision in the inflamed area, but this does not solve the problem at the root. A complete method of operation and cleaning is prescribed after the examination, as a rule, it is galvanocaustic or complete excision. It all depends on the depth and diameter of the canal, as well as the degree of neglect of inflammation.
Given the location, difficulties often arise because the ear fistula is located close to the trunk and branches of the facial nerve. In coma surgery, doctors will prescribe medications and procedures that promote rapid healing and scarring of damaged tissues.
Methods for the prevention of inflammation of the existing fistula have not yet been identified, but children rarely experience pain, and the fistula is rarely detected during this period.
umbilical fistula
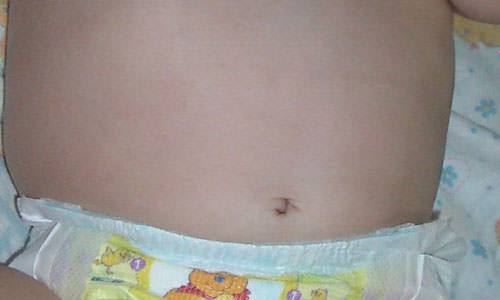
Umbilical fistula is common in newborns
Umbilical fistula, mainly as a congenital phenomenon, is often found in newborns. But, in addition to options for abnormal development, sometimes an acquired fistula is also found. It is formed as a result of surgical operations and inflammations. Fistulas are external and internal, depending on the location of the edge of the canal. An umbilical fistula is often diagnosed at the stage of intrauterine development, during an ultrasound scan. If the change was not noticed during this period, doctors will certainly pay attention to the anomaly during childbirth, during the cutting of the umbilical cord.
Sometimes a fistula is formed due to a violation of the process of obliteration of the embryonic ducts. It is in the first weeks of intrauterine development in a baby that the urinary and bile ducts are connected to the umbilical cord. Subsequent development involves their destruction, but if something goes wrong, a fistula occurs. In an infant, it is detected by the discharge of urine from an opening near the navel or by the presence of a painful swelling.
Diagnosis, in addition to palpation and visual examination, involves some tests. To see the size, exact location and diameter of the cyst, ultrasound and fistulography are performed.
A complete fistula of the navel of a newborn suggests communication between the navel and the small intestine. This is a complex anomaly in which the contents of the intestine are released outside through the fistulous canal. Treatment of such a fistula is reduced to intra-abdominal surgery and removal of embryonic remnants. If the disease is not treated, the inflammatory process can cause serious complications such as internal hernia, intestinal obstruction, and even volvulus of the small intestine.
