The shunt release is an addition to the mains protection device. It is mechanically connected to the circuit breaker. The independent release performs the function of breaking the circuit when it detects factors that can lead to damage to the line and the devices included in it. These include an increase in the current strength above the limit that the cable can withstand, a breakdown of electric current to the ground or the case of a device included in the circuit, as well as a short circuit. This material will help you figure out what circuit breakers are, what types of this device are, and what is the principle of operation of each of them. In addition, we will tell you how to check the performance of these elements.
Automatic safety switch with shunt trip
The shunt trip, as mentioned, is an additional element of the circuit protection device. It allows you to turn off the AB at a distance when voltage is applied to its coil. To return it to its original state, you should press the button on the device that says "Return".
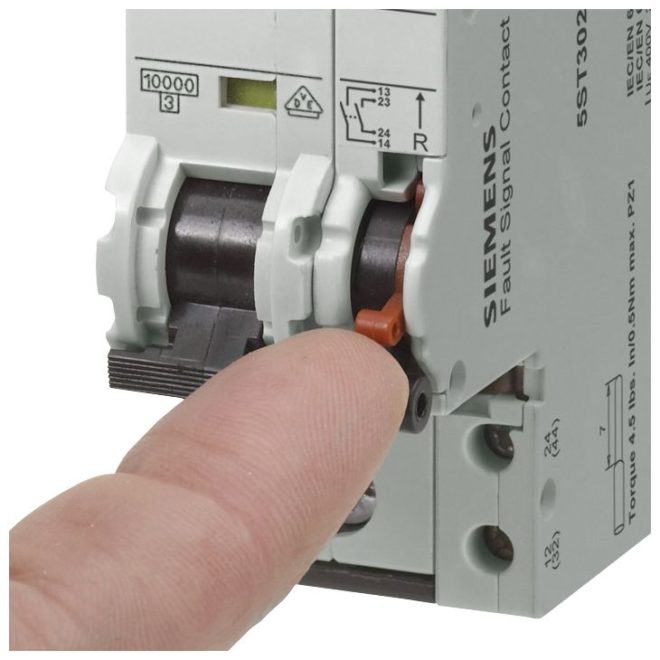

Circuit breakers of this type can be used in single-phase and three-phase networks.
The shunt release is most often used in electrical circuits and automatic switchboards of large facilities. Power supply management in these cases, as a rule, is carried out from the operator's console.
An example of operation of a shunt trip on video:
What triggers an independent trip element?
The shunt release may trip for various reasons. We list the most common ones:
- Excessive decrease or, conversely, an increase in voltage.
- Changing the set parameters or the state of the electric current.
- Violation of the function of automatic switches, failure in operation for an unknown reason.
In addition to independent trip devices, there are similar elements that are part of the circuit breakers. Built-in releases of circuit breakers are divided into thermal and electromagnetic. These devices also help protect the line from excessive loads and short circuits. Let's consider them in more detail.
Thermal release of the circuit breaker
The main element of this device is a bimetallic plate. In its manufacture, two metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion are used.
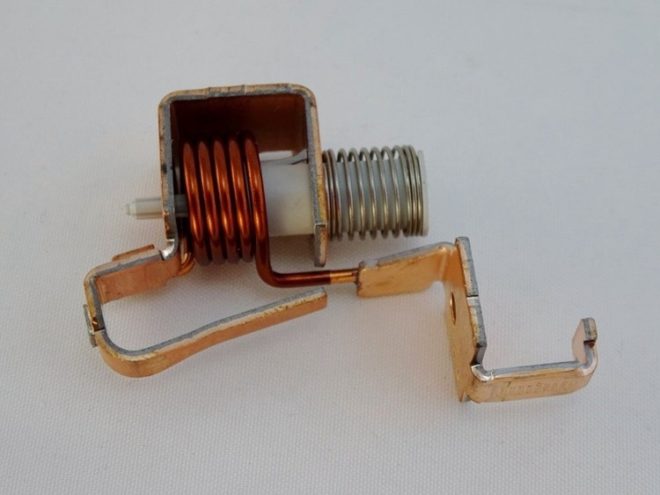
When pressed together, they expand to varying degrees when heated, causing the plate to warp. If the current does not normalize for a long time, then upon reaching a certain temperature, the plate touches the AB contacts, interrupting the circuit and de-energizing the wiring.
The main reason for excessive heating of the bimetallic plate, due to which the thermal release is triggered, is too high a load on a certain section of the line, protected by the machine.
For example, the cross section of the AB output cable going into the room is 1 sq. mm. It can be calculated that it is able to withstand the connection of devices with a total power of up to 3.5 kW, while the strength of the current passing in the line should not exceed 16A. Thus, in this group, you can safely connect a TV and several lighting fixtures.
If the owner of the house decides to include an additional washing machine, an electric fireplace and a vacuum cleaner in the sockets of this room, then the total power will become much higher than what the cable can withstand. As a result, the strength of the current passing through the line will increase, and the conductor will begin to heat up.
Overheating the cable can cause the insulation layer to melt and catch fire.
To prevent this from happening, the thermal release comes into action. Its bimetallic plate heats up along with the metal of the wire, and after a while, bending, turns off the power to the group. When it has cooled down, the protective device can be turned on manually again, having previously unplugged the power cords of the devices that led to the overload. If this is not done, after a while the machine will cut down again.
An example of using a release in fire protection on video:
It is important that the AB rating matches the cable section. If it is less than necessary, then operation will occur even under normal load, and if more, then the thermal release will not respond to a dangerous overcurrent, and as a result, the wiring will burn out.
In order to protect electric motors from prolonged overloads and phase failure, thermal trip relays can also be installed on these units. They are several bimetallic plates, each of which is responsible for a separate phase of the power unit.
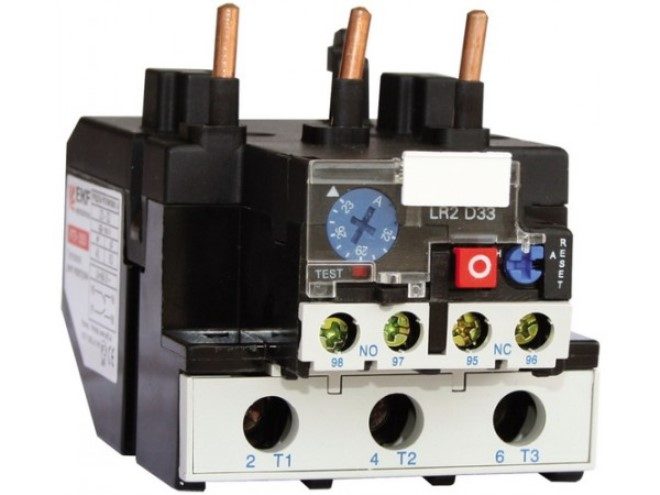

Automatic mains protection switch with electromagnetic release
Having figured out how the machine with a thermal release works, let's move on to the next question. The protective device, the action of which we have just analyzed, does not work immediately (it takes at least a second), so it is not able to effectively protect the circuit from short circuit overcurrents. To solve this problem, an electromagnetic release is additionally installed in the AB.
The releases of electromagnetic type circuit breakers include an inductor (solenoid), as well as a core. When the circuit is operating normally, the flow of electrons passing through the solenoid forms a weak magnetic field, unable to influence the function of the network. When a short circuit occurs, an instantaneous increase in current strength occurs tenfold, and the power of the magnetic field increases proportionally to it. Under its influence, the ferromagnetic core instantly moves to the side, affecting the shutdown mechanism.
Since the process of strengthening the magnetic field during a short circuit occurs in a fraction of a second, the electromagnetic release under its influence is triggered instantly, turning off the mains power. This avoids the serious consequences associated with short circuit overcurrents.
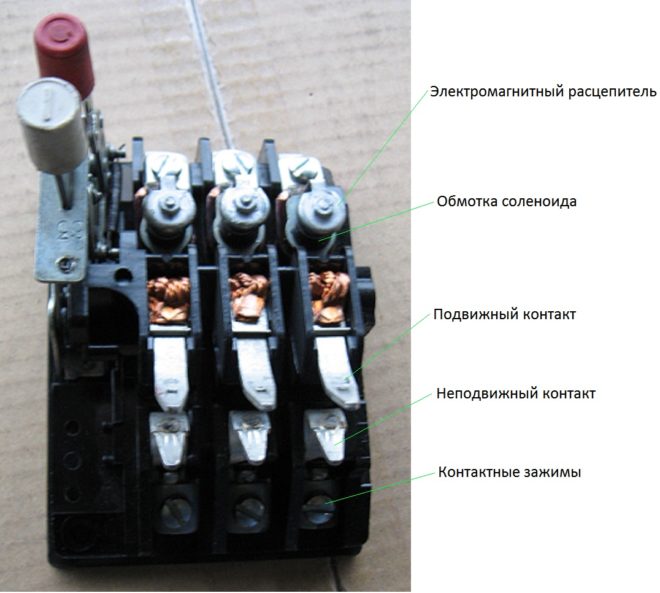
Function test of the releases
Quite often, amateur electricians are interested in whether it is possible to independently check the serviceability of the releases of circuit breakers. It should be said that it is impossible to carry out such testing on your own, and if a novice installer is engaged in it, then an experienced specialist should supervise the work. Here is a step by step guide for this procedure:
- First of all, the surface of the box should be inspected visually to make sure the integrity of the body part.
- Then you need to click the switch lever several times. It should be easy to install in both the on and off position.
- After that, the device is loaded. This is the name of checking the quality of equipment operation in adverse conditions. This stage requires the presence of specialized equipment, and a qualified electrician must be present during its implementation. During the test, the time that elapses from the moment the current rises to the release of the release is recorded.
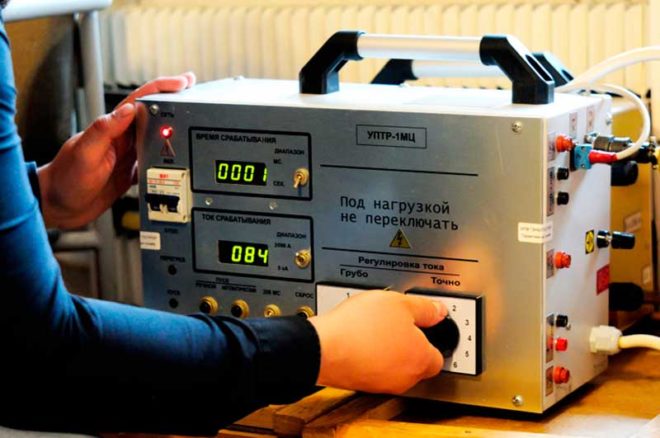

- Finally, a similar test is made on the device from which the casing has been removed.
- During the test for the operation of a thermal release, the time required to disconnect the device under the influence of an increased electric current is fixed.
Checking the serviceability of protective devices in accordance with the requirements of the PUE is carried out only in overalls. As mentioned above, this procedure should be supervised by an experienced specialist.
On the video, the process of installing an independent release in a circuit breaker:
Conclusion
In this article, we dealt with the topic of trip units, talked about what they are and how independent releases, as well as releases built into the circuit breaker, are and work. Now you know how the various types of this equipment work, and what function each of them performs.
